FAQ
WATER
Gray and/or brown staining on the interior of a dishwasher tub can be a calcium or iron build-up. This is a water condition and may re-appear after cleaning.
To remove these stains, do the following:
Fill the wash tank with fresh water and add 50 ml citric acid into the wash tank. (make sure that no detergent is added into the tank during this) Run the dishwasher for sometime (depending on the extent of scale deposit).
Rinse thoroughly by running the dishwasher through another cycle without citric acid but with detergent.
Important – A severe mineral build up may require a second treatment to remove all of the accumulation.
Note: Generally, this procedure should be completed in an empty dishwasher. If dish and glassware have a mineral build up, they can be placed in the dishwasher during this process to remove the accumulated minerals. Never place silverware, aluminum items or other metals in the dishwasher during this process to avoid the possibility of tarnishing. Dishes or glasses with “patterns” should not be left in dishwasher when doing a citric acid treatment. Some”patterns”may be damaged or washed off.
Red, pink or orange stains are most likely caused by a tomato-based product, such as pasta sauce. This stain is not easily removed, but will fade over time.
Note: Citric acid will not have an effect on red, pink or orange stains.
To keep this from happening in the future, remove any excess tomato sauce from your dishes before loading them in the dishwasher.
Rust stains are generally from one of three sources:
Stains from objects placed inside the dishwasher such as pizza pans.
Rust stains appearing to originate on stainless steel parts inside the dishwasher.
Rust from the water supply.
Rust stains from objects placed inside the dishwasher can usually be lightened or removed with a citric acid treatment. Follow the steps described above. To prevent a re-occurrence, keep those objects out of the dishwasher or prevent them from coming in contact with the dishwasher tub.
Rusting of the heating element, stainless steel screws and stainless steel supporting brackets is usually caused by surface iron on those parts. This is cosmetic. The parts themselves are not rusting. The rust may show up on the part, on the tub bottom under the heater or on the tub surrounding the affected part. The rust stain can usually be be lightened or removed with the citric acid treatment described above. After one treatment the rust stains will usually not reappear.
Rust coming from the water supply could be the indication of a plumbing problem requiring the attention of a plumber. The water itself could also contain rust. There are many types of filters available through plumbing contractors that can aid in the control of rust.
Yellow stain This can be removed by wiping it with a mild cleanser and a towel. Use abrasive free cleansers on stainless steel tubs with this problem. An overall yellow staining is probably caused by minerals from the household water supply, coffee or tea and can be cleaned using citric acid.
White stains/film on the tub are caused by hard water minerals. Over time, hard water build-up can cause damage to components of the dishwasher. You may want to consider installing a water softener. · Remove the mineral build up with the citric acid treatment described above.
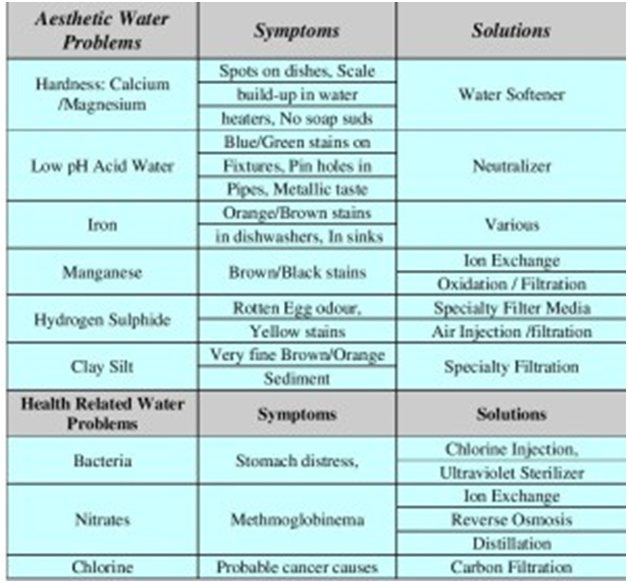
Most of the places in India water have some level of hardness. Hard water can hamper the washing results of your dishwasher and provide less than optimal cleaning results. The Water Softener softens the water being used by the dishwasher providing the best washing results possible. You should use a water softener if the harness of water is more than 40 mg.
Hard water contains dissolved mineral salts – like calcium and magnesium. These minerals can interfere with a detergent’s ability to clean – which is why you may need to use more detergent if your water is hard.
Check it out! You probably have hard water if:
• You suffer from ring around the water storage tanks.
• Soaps and detergents do not lather easily.
• There is white residue around your faucets, boiling pans and drains.
Hardness is caused by
• CaCO3
• MgCO3
• CaSO4
• Ca(HCO3)2
Quantity of above in water decides the degree of hardness. Water is soft up to 40 mg/L, moderately hard up to 120 mg/L and hard above 120 mg/L of calcium hardness. If hardness is more than 40 mg/L, water softener should be used Since water hardness varies from city to city, the easiest way to know if you have it is to call your local water testing lab and have water tested.
Different units of water hardness are:
Mg/L
German Degree
English Degree
French Degree
The minerals contained in the hard water settle out as an unsightly deposit of hardness scale whenever the water is heated, or when cold standing water evaporates.
Examples of this are:
• Unsightly white marks, stains and scale deposits
• Scale deposits leading to premature failures of water heating elements
• Clogging of pipe work
• Water hardness also makes it difficult to get a good lather; so much more detergent is required for washing. Hard water increases detergent requirement by 50% and creates soap scum.
• Dishes and glasses look dull or smeared even after washing.
- Cost Savings in service, maintenance and replacements of spare parts like heaters, solenoid valves etc.
- Improved Efficiency of hot water and heating systems (Just 1.6 mm of scale build-up in heating systems will cause a 12% loss in heating efficiency.
- Saves Time – Independent studies have confirmed that considerable cleaning time is saved with softened water
- Water chemistry is very complex. Water is the universal solvent. It dissolves a little bit of everything it comes in contact with. Therefore water problems and treatment methods will vary from region to region and from well to well depending on the Geology, or more specifically what the water has been in contact with before it enters your home or business.
TREATING WATER PROBLEMS