FAQ
DISHWASHERS
There are four important factors for good wash performance in all areas of your dishwasher:
- Loading the dishes correctly
- Water temperature of the machine
- Detergent and Rinse aid
- Water inlet pressure
- Quality of water
Loading of dishes
Use Correct Rack
- The glass rack is for glasses.
- The peg rack is for plates, trays thalis etc.
- The flatware rack is for cutlery, large bowls etc.
- All items should be placed facing down so that no water is collected during washing process, plates should be placed inclined facing up.
Water temperature
- The entering water must be at least 20 degrees Celsius and not more than 60 degrees Celsius.
- The wash temperature of the machine is 60 – 65 deg. C
- The final rinse temperature of the machine is 82 – 87 deg. C
Detergent and Rinse aid
- It is important to use the correct type of detergent
- Use detergents meant for commercial dishwasher application only.
- Washmatic recommends Washmate Plus detergent and Rinsemate Ultra rinse agent
- Rinse agents helps water to sheet off glass and dinnerware which prevents spotting and improves overall drying performance.
Water inlet pressure
The water inlet pressure should be 2 – 4 bar (dynamic pressure)
Quality of water
The water used for dish washing should be of potable quality with hardness less that 40 Mg
Check the water pressure.
The dynamic water pressure to the dishwasher should be 2 to 4 bar.
Check the wash cycle selection.
Select the appropriate cycle for the dish load. Selecting a short or light wash cycle may save water and energy, but may not provide proper wash action for a heavily soiled load. If food soils remain on the dishware after the cycle, a longer cycle may be required. Please consult the Owner’s Manual.
Check the water temperature.
Proper water temperature is essential to achieve optimum results from your dishwasher and the detergent. Hot water is needed to dissolve and activate the detergent so that it can loosen and remove common food soils. Wash water temperature should be between 55 to 65 deg C and rinse water temperature between 82 to 87 deg C
The hot water heater should be set to deliver at least 20 degree C water to the dishwasher
To check the water temperature, run the hot water at the kitchen sink and measure the temperature of the running water with a candy or meat thermometer. Adjust the temperature of the water heater accord
Check the amount of detergent and the water hardness.
The amount of detergent needed depends upon: water hardness, the amount of food soils left on the dish load, and the temperature of the water going into the dishwasher. Do not use liquid detergents not made for automatic dishwashers.
Use a Rinse Agent.
Rinse agents promote wash and dry performance by causing the water to sheet off of the ware inside the dishwasher. This prevents water spots from forming on the glassware and dishware.
Check the dishwasher loading.
Make sure dishes are loaded properly to insure that water can reach all of the soiled surfaces in both racks. Please consult the Owner’s Manual.
Here are some common loading guidelines for assistance:
Place glasses with the open end facing downward to allow proper washing action.
Do not allow flatware to nest. This prevents proper water distribution between the surfaces. Load flatware, except knives, with some handles up and some down to prevent nesting. For safety, knives should always be loaded handles up.
Do not block wash system parts including spray arms and towers located at top / bottom.
Excessive amounts of food may clog the dishwasher filters and reduce wash performance.
In models without extending wash towers, the spray arm may be removed to check the filter underneath. Inspect the fine filter. It should be clean. If not, clean out all the filters and spray arms. To prevent this from happening, scrape dishes before placing them in the dishwasher and pre-rinse the dishes to remove solid particles.
A dishwasher will not normally retain odors. Odors present for extended periods of time should be considered abnormal.
Food Odors: If abnormal odors are observed in the dishwasher, check for food particle residue on the tub bottom / filters. If any particles are found, remove them. Also, check the spray arm jets. If any jets are blocked, open the nozzles clean the blocked jets. Be careful not to damage the jets in any way as that will affect wash performance.
Also, check the spray arm jets. If any jets are blocked, open the nozzles clean the blocked jets. Be careful not to damage the jets in any way as that will affect wash performance.
After performing the above operations, run the dishwasher with detergent and nothing else inside. This should flush out the machine and eliminate the cause of food residue odor.
To prevent this from reoccurring, scrape off plates and per-rinse properly before placing them in the dishwasher. Remember, the dishwasher is not a food disposer.
Odor from dirty water in the tub: Dirty water building up in the dishwasher between uses is an installation problem caused by an improperly installed drain hose. The installation instructions require either an air gap or a high drain loop. When this problem is observed, the drain hose was installed without either a high drain loop or an air gap or is is connected at a higher level than recommended.
As tempting as it is to throw everything in and get that load going, there will always be some items that are better suited to washing by hand. The force and heat of the water – and even the detergent – can damage fragile pieces. If possible, check with the manufacturer to see if the item is “dishwasher safe” – although this may not be easy in the case of older items. As an alternative, your dishwasher manual may give suggestions for the wash ability of delicate items.
| Still in doubt? | |
| To be safe, unless the manufacturer can tell you otherwise, you’ll probably want to hand wash these items: | |
|
|
No! Not only would this mean soapy suds all over your floor . . . but there’s also a technical reason why this doesn’t work. The suds created by a hand dishwashing detergent interfere with the mechanical action of the dishwasher – they “smother” the water action that’s necessary for effective cleaning. So leave hand dishwashing liquid at sink-side!
Washmatic dishwashers are designed to save huge amounts of water, chemical, time and labour costs. Washmatic improves the hygiene levels of both the washing area and the cutlery. It also minimises chipping and breakage of expensive cutlery during washing, thus saving huge amounts there too.
To check how much can a washmatic dishwasher can save for you, please check the “savings guide” in “support” menu of our website, you may use this direct link for the same https://washmaticindia.com/saving-guide.php
You can see that the cost of the machine can be recovered in less than a years time. The per day savings for washing 2000 plates per day is around Rs 1250/-
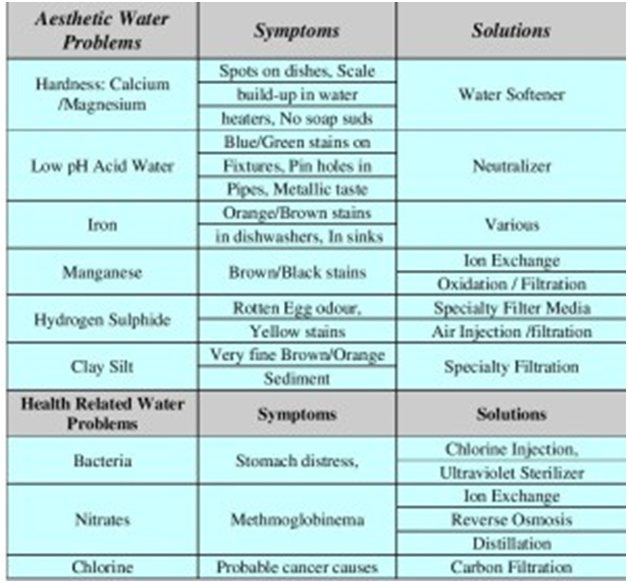
WATER
Gray and/or brown staining on the interior of a dishwasher tub can be a calcium or iron build-up. This is a water condition and may re-appear after cleaning.
To remove these stains, do the following:
Fill the wash tank with fresh water and add 50 ml citric acid into the wash tank. (make sure that no detergent is added into the tank during this) Run the dishwasher for sometime (depending on the extent of scale deposit).
Rinse thoroughly by running the dishwasher through another cycle without citric acid but with detergent.
Important – A severe mineral build up may require a second treatment to remove all of the accumulation.
Note: Generally, this procedure should be completed in an empty dishwasher. If dish and glassware have a mineral build up, they can be placed in the dishwasher during this process to remove the accumulated minerals. Never place silverware, aluminum items or other metals in the dishwasher during this process to avoid the possibility of tarnishing. Dishes or glasses with “patterns” should not be left in dishwasher when doing a citric acid treatment. Some”patterns”may be damaged or washed off.
Red, pink or orange stains are most likely caused by a tomato-based product, such as pasta sauce. This stain is not easily removed, but will fade over time.
Note: Citric acid will not have an effect on red, pink or orange stains.
To keep this from happening in the future, remove any excess tomato sauce from your dishes before loading them in the dishwasher.
Rust stains are generally from one of three sources:
Stains from objects placed inside the dishwasher such as pizza pans.
Rust stains appearing to originate on stainless steel parts inside the dishwasher.
Rust from the water supply.
Rust stains from objects placed inside the dishwasher can usually be lightened or removed with a citric acid treatment. Follow the steps described above. To prevent a re-occurrence, keep those objects out of the dishwasher or prevent them from coming in contact with the dishwasher tub.
Rusting of the heating element, stainless steel screws and stainless steel supporting brackets is usually caused by surface iron on those parts. This is cosmetic. The parts themselves are not rusting. The rust may show up on the part, on the tub bottom under the heater or on the tub surrounding the affected part. The rust stain can usually be be lightened or removed with the citric acid treatment described above. After one treatment the rust stains will usually not reappear.
Rust coming from the water supply could be the indication of a plumbing problem requiring the attention of a plumber. The water itself could also contain rust. There are many types of filters available through plumbing contractors that can aid in the control of rust.
Yellow stain This can be removed by wiping it with a mild cleanser and a towel. Use abrasive free cleansers on stainless steel tubs with this problem. An overall yellow staining is probably caused by minerals from the household water supply, coffee or tea and can be cleaned using citric acid.
White stains/film on the tub are caused by hard water minerals. Over time, hard water build-up can cause damage to components of the dishwasher. You may want to consider installing a water softener. · Remove the mineral build up with the citric acid treatment described above.
Most of the places in India water have some level of hardness. Hard water can hamper the washing results of your dishwasher and provide less than optimal cleaning results. The Water Softener softens the water being used by the dishwasher providing the best washing results possible. You should use a water softener if the harness of water is more than 40 mg.
Hard water contains dissolved mineral salts – like calcium and magnesium. These minerals can interfere with a detergent’s ability to clean – which is why you may need to use more detergent if your water is hard.
Check it out! You probably have hard water if:
• You suffer from ring around the water storage tanks.
• Soaps and detergents do not lather easily.
• There is white residue around your faucets, boiling pans and drains.
Hardness is caused by
• CaCO3
• MgCO3
• CaSO4
• Ca(HCO3)2
Quantity of above in water decides the degree of hardness. Water is soft up to 40 mg/L, moderately hard up to 120 mg/L and hard above 120 mg/L of calcium hardness. If hardness is more than 40 mg/L, water softener should be used Since water hardness varies from city to city, the easiest way to know if you have it is to call your local water testing lab and have water tested.
Different units of water hardness are:
Mg/L
German Degree
English Degree
French Degree
The minerals contained in the hard water settle out as an unsightly deposit of hardness scale whenever the water is heated, or when cold standing water evaporates.
Examples of this are:
• Unsightly white marks, stains and scale deposits
• Scale deposits leading to premature failures of water heating elements
• Clogging of pipe work
• Water hardness also makes it difficult to get a good lather; so much more detergent is required for washing. Hard water increases detergent requirement by 50% and creates soap scum.
• Dishes and glasses look dull or smeared even after washing.
- Cost Savings in service, maintenance and replacements of spare parts like heaters, solenoid valves etc.
- Improved Efficiency of hot water and heating systems (Just 1.6 mm of scale build-up in heating systems will cause a 12% loss in heating efficiency.
- Saves Time – Independent studies have confirmed that considerable cleaning time is saved with softened water
- Water chemistry is very complex. Water is the universal solvent. It dissolves a little bit of everything it comes in contact with. Therefore water problems and treatment methods will vary from region to region and from well to well depending on the Geology, or more specifically what the water has been in contact with before it enters your home or business.
TREATING WATER PROBLEMS
SERVICE
In the event your Washmatic machine is in need of service within the warranty period, it is required that you contact us to obtain a complaint registration number. A Customer Service Representative will assign a complaint registration number.
The customer care centre no. is +91 99100 88680
email — [email protected]
If your Washmatic machine is in need of repair and the machine is outside the warranty period it is required that you contact us to obtain a complaint registration number. A Customer Service Representative will assign a complaint registration number. You will have to approve the visit charges for inspection of the defective machine and after that the representative will visit you. After inspecting the machine, washmatic representative will determine the necessary repairs needed and will provide you with an estimate including the shipping costs to you.
The customer care centre no. is +91 99100 88680
email — [email protected]
Our call centre number is +91 99100 88680
HYGIENE
A dishwasher will not normally retain odors. Odors present for extended periods of time should be considered abnormal.
Food Odors: If abnormal odors are observed in the dishwasher, check for food particle residue on the tub bottom / filters. If any particles are found, remove them. Also, check the spray arm jets. If any jets are blocked, open the nozzles clean the blocked jets. Be careful not to damage the jets in any way as that will affect wash performance.
Also, check the spray arm jets. If any jets are blocked, open the nozzles clean the blocked jets. Be careful not to damage the jets in any way as that will affect wash performance.
After performing the above operations, run the dishwasher with detergent and nothing else inside. This should flush out the machine and eliminate the cause of food residue odor.
To prevent this from reoccurring, scrape off plates and per-rinse properly before placing them in the dishwasher. Remember, the dishwasher is not a food disposer.
Odor from dirty water in the tub: Dirty water building up in the dishwasher between uses is an installation problem caused by an improperly installed drain hose. The installation instructions require either an air gap or a high drain loop. When this problem is observed, the drain hose was installed without either a high drain loop or an air gap or is is connected at a higher level than recommended.
| Job | Cleaning agent | Comments |
| Routine cleaning | Soap, ammonia , detergent medallion | Apply with cloth or sponge |
| Fingerprints & smears | Arcal 20* , Lac –O-NU Ecoshine* | Provides barrier film |
| Stubborn stains & discoloration | Cameo*, talc, Zud First impression | Rub in direction of polish lines |
| Grease & fatty acids, blood , burnt on foods | Easy off* , De – Grease it oven aid* | Excellent removal on all finishes |
| Grease & oil | Any good commercial detergent | Apply with sponge of cloth |
| Restoration / Passivation | Benefit* , Super Sheen* |
* Diversey / Ecolab products
SAVINGS
Washmatic dishwashers are designed to save huge amounts of water, chemical, time and labour costs. Washmatic improves the hygiene levels of both the washing area and the cutlery. It also minimises chipping and breakage of expensive cutlery during washing, thus saving huge amounts there too.
To check how much can a washmatic dishwasher can save for you, please check the “savings guide” in “support” menu of our website, you may use this direct link for the same https://washmaticindia.com/saving-guide.php
You can see that the cost of the machine can be recovered in less than a years time. The per day savings for washing 2000 plates per day is around Rs 1250/-
CHEMICALS
No! Not only would this mean soapy suds all over your floor . . . but there’s also a technical reason why this doesn’t work. The suds created by a hand dishwashing detergent interfere with the mechanical action of the dishwasher – they “smother” the water action that’s necessary for effective cleaning. So leave hand dishwashing liquid at sink-side!
Check the directions on the label of the detergent can for the recommended amount. You can also refer to the dishwasher’s User Manual.
The recommended dosage of Washmate Plus detergent is 3 ml per 1 litre of wash tank water.
Here’s an additional tip: If you have hard water, you may need to use a little more detergent to get the best “clean” . . . and if your water is soft, do the opposite and try using a little less detergent.
A rinse agent is an additive that makes water “wetter” – meaning that the water sheets off dishes more readily and rinses away residue. That translates into fewer water spots – making a rinse agent especially helpful if you have mineral-rich hard water. And as an added bonus, rinse agents also help dishes dry more quickly.
Normally, you simply scrape food particles from dishes and pre-rinse before loading them in the dishwasher, making presoaking unnecessary. But if you’re dealing with dried-on, baked-on food or grease, try pre-soaking in a hand dishwashing detergent and water solution. Check the label on your automatic dishwasher detergent. Some of them are appropriate for pre-soaking too.
Simply put: no. While some household cleaning products are multi-purpose, automatic dishwasher detergent is formulated specifically for use in a dishwasher. In fact, it could damage other surfaces – so use it only as intended!
Yes, automatic dishwasher detergent is safe when used and stored according to the directions on the label. But because accidents can happen, it’s important to keep all cleaning products out of the reach of children and pets to avoid accidental ingestion.
No. Automatic dishwasher detergent is formulated to go down the drain with the wash water . . . and from there, it’s safely treated in both municipal sewage treatment facilities and home septic systems.
You should use low foaming type detergent meant for commercial dishwasher application.
Automatic Dishwasher Detergents provide the chemical energy to help remove food soil from all types of cooking and serving items. Unlike hand dishwashing products, these must be of non foaming type. Suds (foam) cushion the mechanical cleaning action of the water and result in suds overflow from the machine.
In addition, automatic dishwasher detergents should inhibit foam that certain protein-containing foods, such as egg and milk, create. They must also soften water to prevent insoluble deposits, loosen and hold soil in suspension, leave items clean and grease-free so they rinse and dry without spots, and be safe for a wide variety of dishes, glassware, utensils, etc.
Surfactants or surface active agents loosen soil and emulsify fats, help hold them in suspension, and leave surfaces clean and free from spots and film. Specially developed surfactants having the lowest foaming characteristic are used.
Phosphates tie up water hardness minerals (primarily calcium and magnesium); so the minerals do not interfere with cleaning or deposit on surfaces. Phosphates also help keep food soil particles in suspension after removal from the soiled surfaces and prevent their re-deposition.
Chlorine or Oxygen Bleaches are added to help prevent spots by leaving a cleaner surface than would be obtained with either surfactants or phosphates alone. The very small amount of bleach helps break own protein soils and aids in removing stains such as coffee or tea.
Corrosion Inhibitors, such as sodium silicate, help provide protection for the dishwasher and the wide variety of materials that are washed. Some materials still should not be washed in the automatic dishwasher (see Washmatic Know more). The corrosion inhibitors also act as soil suspending agents and as an important source of alkalinity.
Enzymes are naturally occurring proteins that help break down food and soil residue into small particles. The small particles are then washed away.
Special Additives, such as sodium aluminate, boric oxide or aluminium phosphate may be used to inhibit the removal of over glaze and pattern from fine china. Sometimes antifoams are added to reduce foaming.
Additional Alkalis, such as sodium carbonate, hydroxide or trisodium phosphate, may be used to aid in handling greasy food soils. Polymers help prevent film build-up from hard water.
Colorants are added to lend individuality and an appealing appearance to the product.
Processing Aids, generally inert materials, allow the active ingredients to be combined into a usable form.
Fragrance covers the chemical odour of the base product and stale food odours that might come from the dishwasher.
STAINLESS STEEL
Stainless steel, also known as Inox steel or Inox from French “inoxydable“, is a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5% chromium content by mass.
Stainless steel does not readily corrode, rust or stain with water as ordinary steel does, but despite the name it is not fully stain-proof, most notably under low oxygen, high salinity, or poor circulation environments. There are different grades and surface finishes of stainless steel to suit the environment the alloy must endure. Stainless steel is used where both the properties of steel and resistance to corrosion are required.
Stainless steel differs from carbon steel by the amount of chromium present. Unprotected carbon steel rusts readily when exposed to air and moisture. This iron oxide film (the rust) is active and accelerates corrosion by forming more iron oxide, and due to the greater volume of the iron oxide this tends to flake and fall away. Stainless steels contain sufficient chromium to form a passive film of chromium oxide, which prevents further surface corrosion by blocking oxygen diffusion to the steel surface and blocks corrosion from spreading into the metal’s internal structure, and due to the similar size of the steel and oxide ions they bond very strongly and remain attached to the surface.
Passivation only occurs if the proportion of chromium is high enough and oxygen is present.
Contrary to popular belief, Stainless Steels are susceptible to rusting.
Corrosion on metals is everywhere. We recognize it quickly on iron and steel as unsightly yellow/orange rust. Such metals are called “active” because they actively corrode in the natural environment.
Stainless steels are passive metals because they contain other metals, like chromium and nickel.
400 series stainless steels contain chromium while 300 series contain both chromium and nickel.
Metals are crystalline solids made up ion atom arrangements like tinker toys. With 12-30% chromium, an invisible passive film covers the steels surface acting as shield against corrosion. The metal becomes “passive” toward corrosion.
As long as the film is intact; not broken or contaminated, the metal is passive and stain-less.
There are three basic things which can break down your stainless steel’s passivity layer and allow corrosion to rear its ugly head.
- Mechanical abrasion
- Deposits & water
- Chlorides
Mechanical abrasion means those things that will scratch the steel’s surface . Steels pads , wire brushes and scrapers are prime examples.
Water comes out of our tap in varying degree of hardness. Depending on what part of the country you live in, you may have hard or soft water. Hard water may leave spots. Also when heated, hard water leaves deposits behind that if left to sit, will break down the passive layer and rust your stainless steel. Other deposits from food preparation and service must be properly removed.
Cholorides are found nearly everywhere. They are in water , food and table salt. One of the worst perpetrator of chlorides can come from household and industrial cleaners.
In a nutshell:- Stainless Steels do rust when
Passivity (film Shield) breaks down
By scraps and scratches
By deposits and chlorides
Here are a few steps that can help prevent stainless steel rust.
- Use the proper tools : when cleaning you stainless steel products, take care to use non-abrasive tools. Soft cloths and plastic scouring pads will not harm the steels passive layer. Stainless steel pads can also be used but the scrubbing motion must be in the direction of the manufacturers polishing marks. Step 2 tells you how to find the polishing marks.
- Clean with the polish lines : some stainless steels come with visible polishing lines or “grain.” When visible lines are present, you should always scrub in a motion that is parallel to them.When the grain cannot be seen play it safe and use a soft cloth or plastic scouring pad.
- Use alkaline, alkaline chlorinated or non-chloride containing cleaners: while many traditional cleaners are loaded with chlorides, the industry is providing an ever increasing choice of non-chloride cleaners. Is you are not sure of your cleaner’s chloride content contact your cleaner supplier. If they tell you that your present cleaner contains chlorides, ask if they have an alternative. They probably will. Also, avoid cleaners containing quaternary salts as they also can attack stainless steel and cause pitting and rusting.
- Treat you water : Though this is not always practical, softening hard water can do much to reduce deposits. There are certain filters that can be installed to remove distasteful and corrosive elements. Salts in a properly maintained water softener are your friend. If you are not sure of the proper water treatment, call a treatment specialist.
- keep your food equipment clean: Use alkaline , alkaline chlorinated or non chloride cleaners at recommended strength. Clean frequently to avoid build up of hard, stubborn stains. If you boil water in your stainless steel equipment, remember the single most likely cause of damage is chlorides in the water. Heating cleaners that contain chlorides has a similar effect.
- Rinse , Rinse , Rinse: If chlorinated cleaners are used you must rinse, rinse, rinse and wipe dry immediately. The sooner you wipe off standing water ,especially when it contains cleaning agents, the better. After wiping the equipment down, allow it to air dry for the oxygen helps maintain the stainless steels passivity film.
- Never use hydrochloric acid (Muriatic acid) on stainless steel
- Regularly restore / passivate stainless steel
| Job | Cleaning agent | Comments |
| Routine cleaning | Soap, ammonia , detergent medallion | Apply with cloth or sponge |
| Fingerprints & smears | Arcal 20* , Lac –O-NU Ecoshine* | Provides barrier film |
| Stubborn stains & discoloration | Cameo*, talc, Zud First impression | Rub in direction of polish lines |
| Grease & fatty acids, blood , burnt on foods | Easy off* , De – Grease it oven aid* | Excellent removal on all finishes |
| Grease & oil | Any good commercial detergent | Apply with sponge of cloth |
| Restoration / Passivation | Benefit* , Super Sheen* |
* Diversey / Ecolab products
Passive Film Breakdown
If the passive film of your stainless steel has been broken, your equipment will begin the long walk down the dark road of corrosion. At its end; rust.
The first signs are on the microscopic level. If you were to look at them under a microscope or through a magnifying glass, you would see small pits and cracks staring back at you. Given time, these pits and cracks will grow and deepen while all the time exuding unsightly, red-orange rust. More severe and visible cracking can also take place.